# Query Log
The query logs provide a platform user with direct access to specific user queries and sessions. User queries are logged and scrubbed of any extra data (i.e., log-system data, business logic payloads, etc.) before they are passed to the query response payload. They are stored inside log-stash and retrieved using OpenSearch.
The Query Log page has numerous features that a platform user can utilize to keep improving an AI model’s quality with real end-user data. The following sections describe these features in more detail:
# Filters
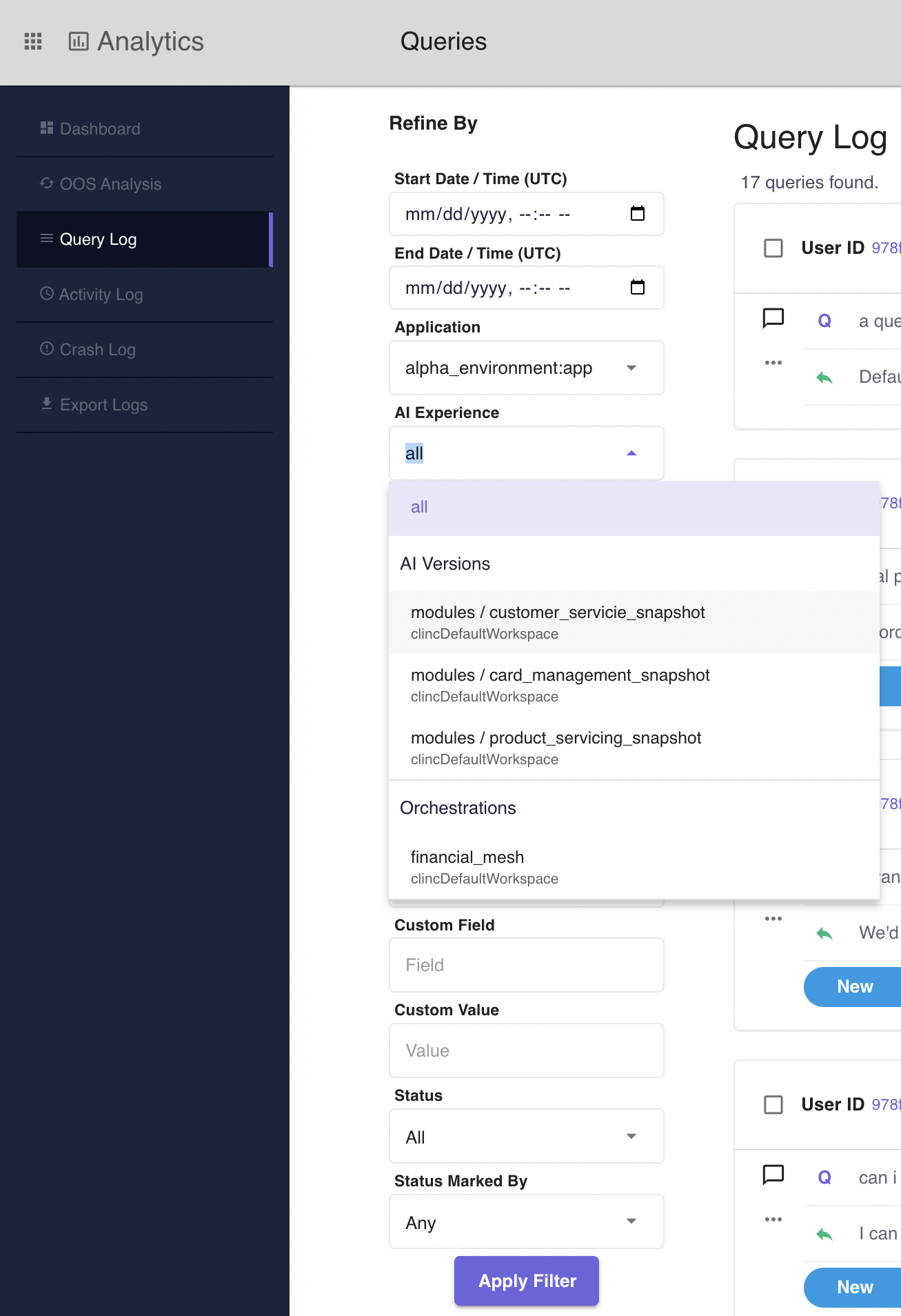
Queries can be filtered by the following criteria. The following four filters are applied in order with respect to the following heirarchy. Application, Experience, Competency, and Device. In the example screenshots below, there is an application selected and the AI Experiences dropdown is expanded, only showing experiences associated with the application. Competencies dropdowns should only have values corresponding with remaining experiences and devices dropdown should only have values corresponding with remaining competency values. If any value is changed, the values below it in the heirarchy will be reset to the value 'all'. See the glossary below for a definition of what each of the filters can be used for.
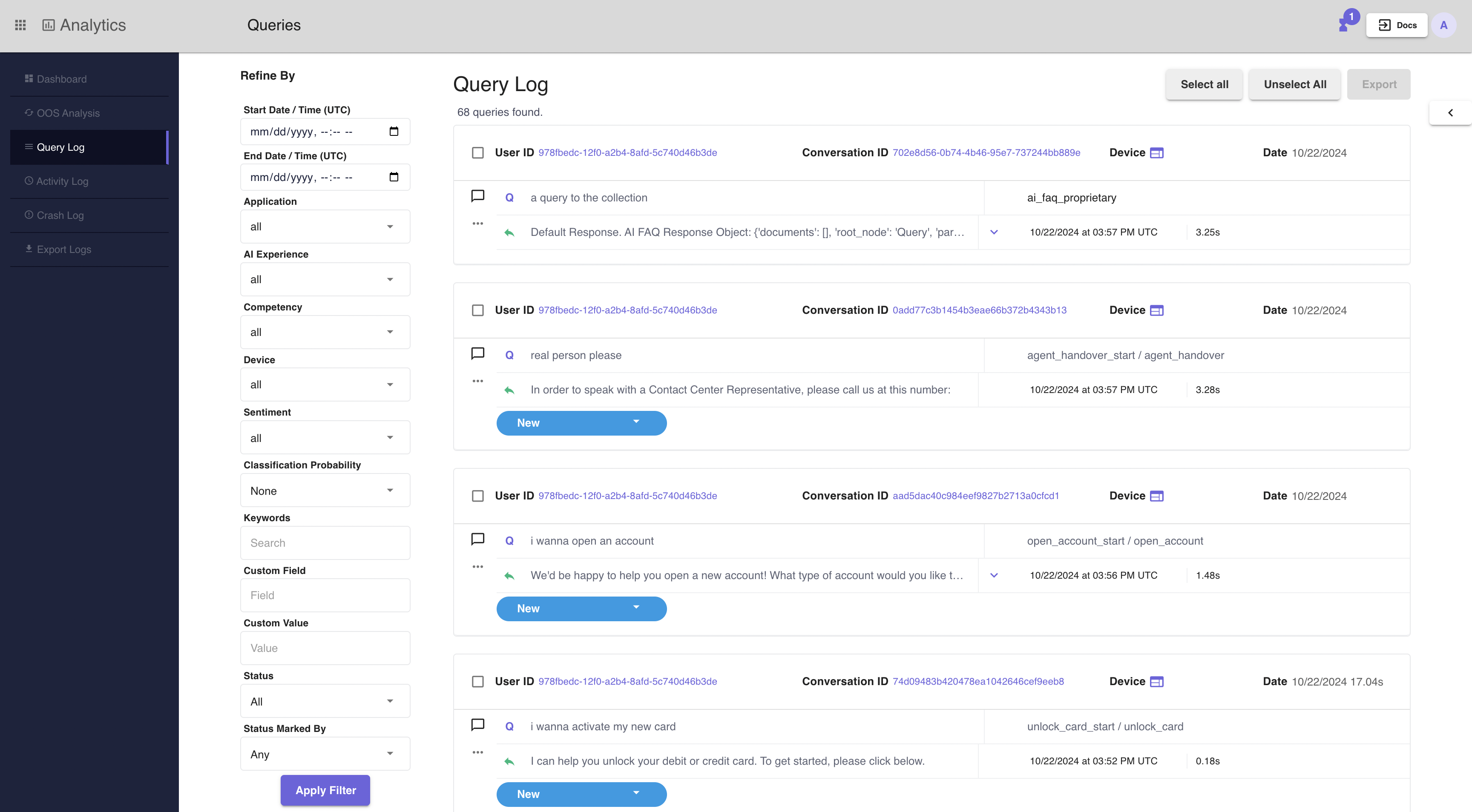
- Date and time: Sort the queries by choosing a specific time frame. The time is consistent with the system timezone that is configured in Settings.
- Application: Selecting an application filters the queries seen in query log to queries that are only associated with the selected application.
- Experience: Selecting an experience filters queries seen in the query log to queries that are associated with the selected experience. If an application is selected, a user selecting an application will only see experiences associated with the selected application in the dropdown for selection.
- Competency: Choose to view queries from a specific competency.
- Device: Choose to view queries by devices such as web, mobile, or smart devices.
- Sentiment: Choose to show only positive or negative user queries.
- Classification Probability: Sort queries by confidence scores.
- Keywords: Search queries with specific keywords.
- Custom Field: A user can use this field to search queries for any custom field in the query response JSON payload. For example, one could filter by
intent, and the value can beclean_hello_start. - Custom Value: The associated value to the Custom Field.
- Status: Filter queries by one of the following statuses: New, Misclassified, Out of Scope, Flagged or Correct.
- Status Marked By: Sort queries by the platform user who set the query status.
# Assign Status and Add Notes
This feature is designed so a user can annotate the query log data and generate new test cases.
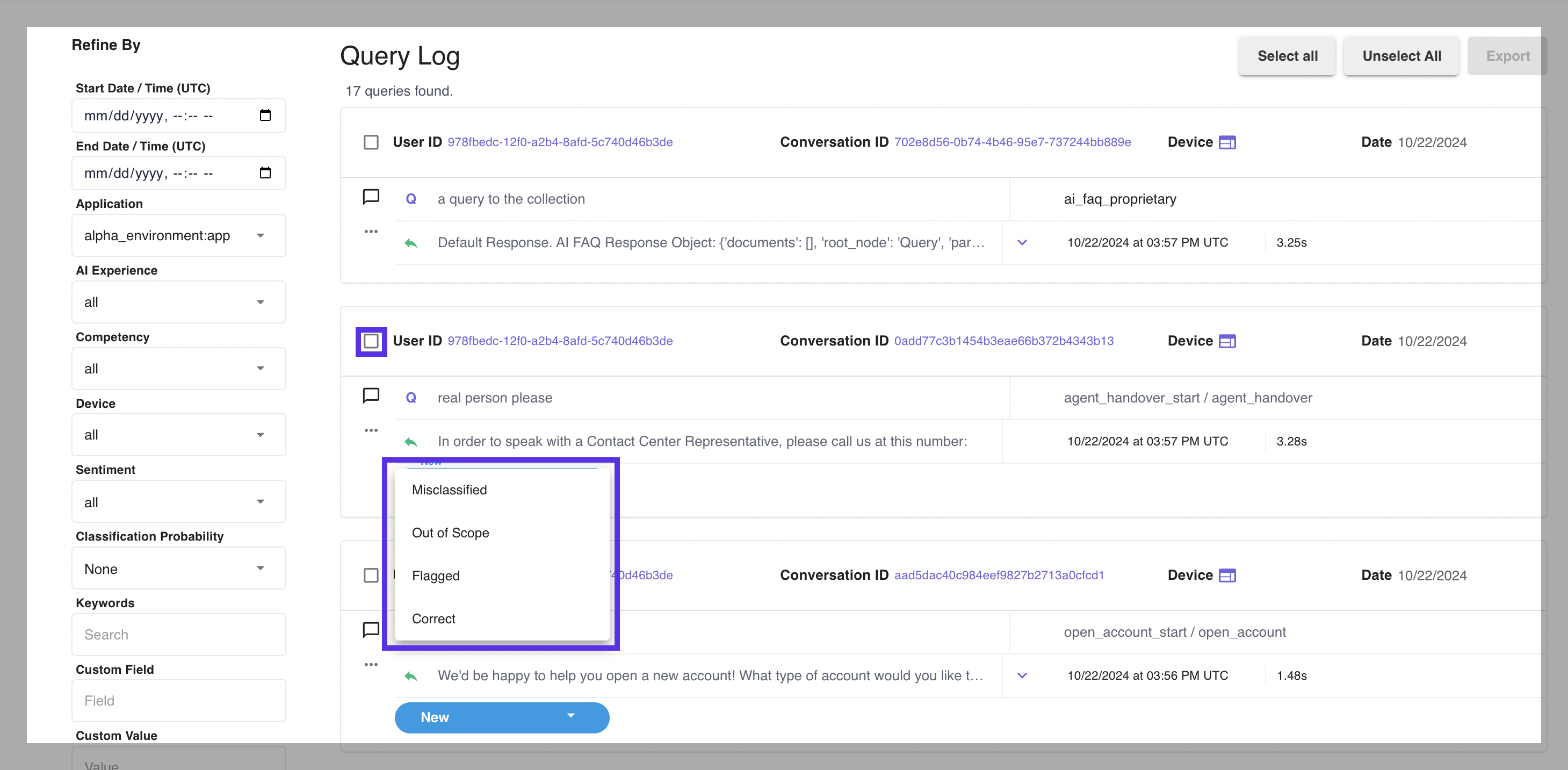
The available types of status are as follow:
- New: The default status of when a new query is added to query logs. It cannot be set by users.
- Misclassified: Used to label queries that are not classified correctly.
- Reclassified: A query is set to “Reclassified“ automatically when a user uses the Correct Classification feature. Users cannot set it without using Correct Classification.
- Out of Scope: Used to label queries that failed to be classified.
- Flagged: Used to label queries that need to be revisited.
- Correct: Used to label queries that are classified correctly.
You can also make notes to the queries by clicking the chat bubble next to each query.
# Correct Classification
If an utterance is misclassified, don't panic! It can mean that the utterance will serve as an excellent guide for AI model quality improvement. The Correct Classification is the tool to accomplish the goal.
To correct the intent of the query,
- Navigate to the
next to the query, select Correct Classification.
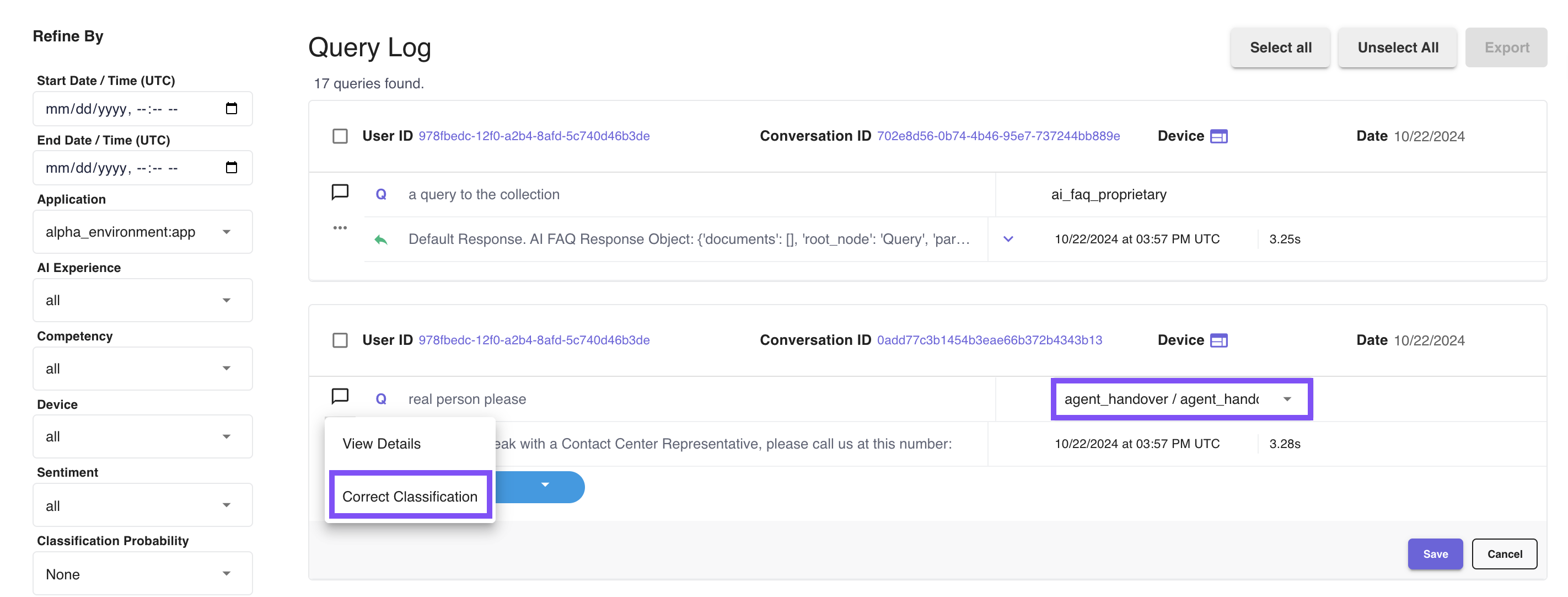
- In the intent/competency dropdown menu, select the correct intent and competency.
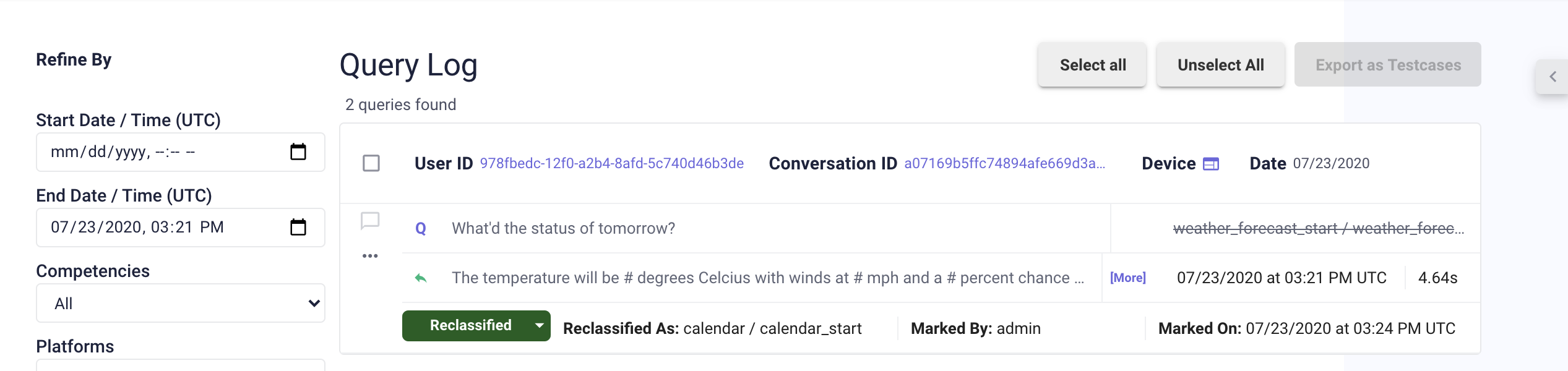
Note: A user will be able to see the comparison between the original intent and reclassified intent, the platform user who modified it, and the timestamp.
Queries can be exported as a new test case at this point.
# Export Queries as Test Cases
When one is ready to export the queries as test cases, they should select the queries they wish the export.
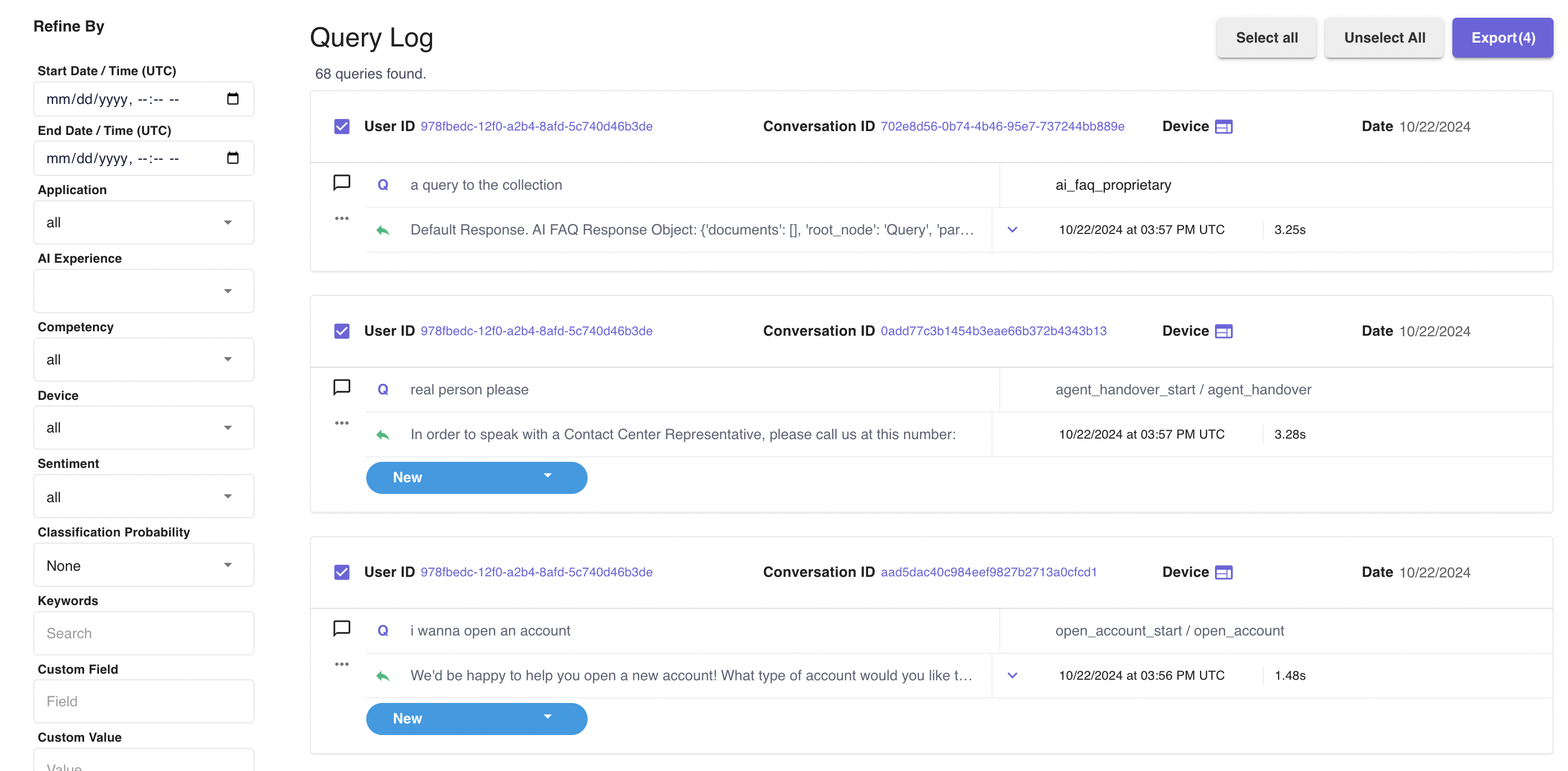
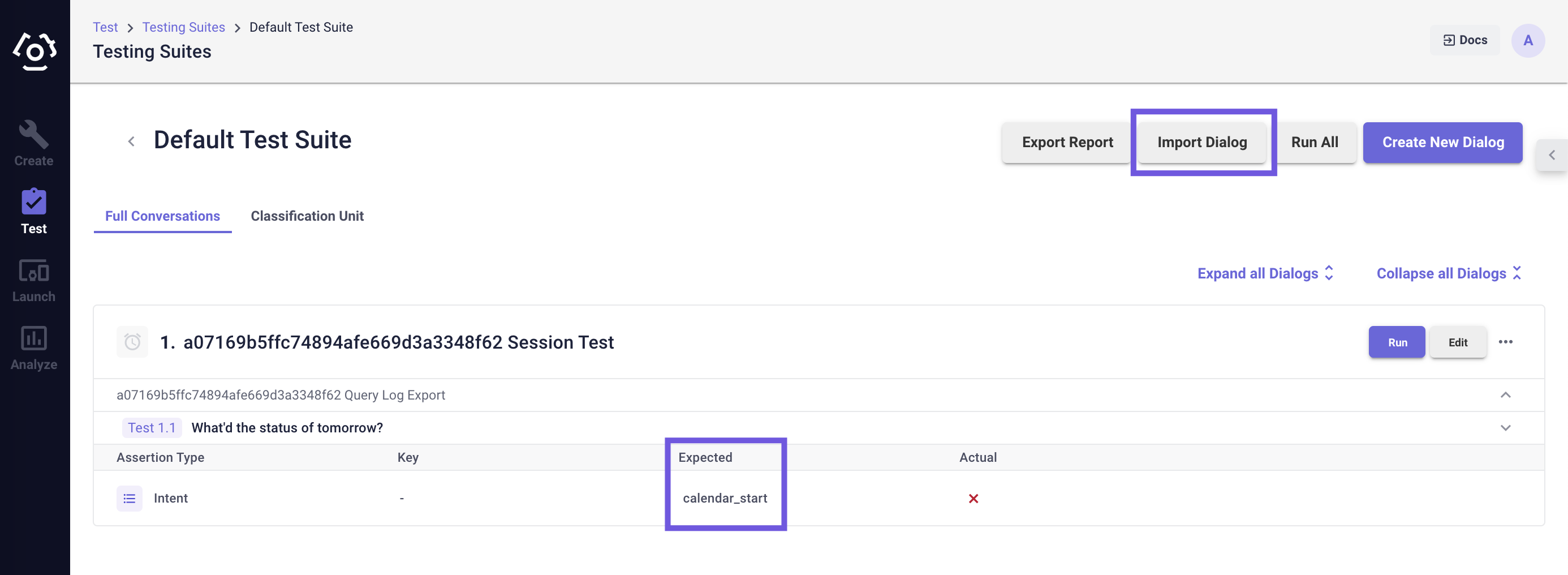
Navigate to the Testing tab, open the test suite designated to the AI version, and import the JSON file exported earlier.
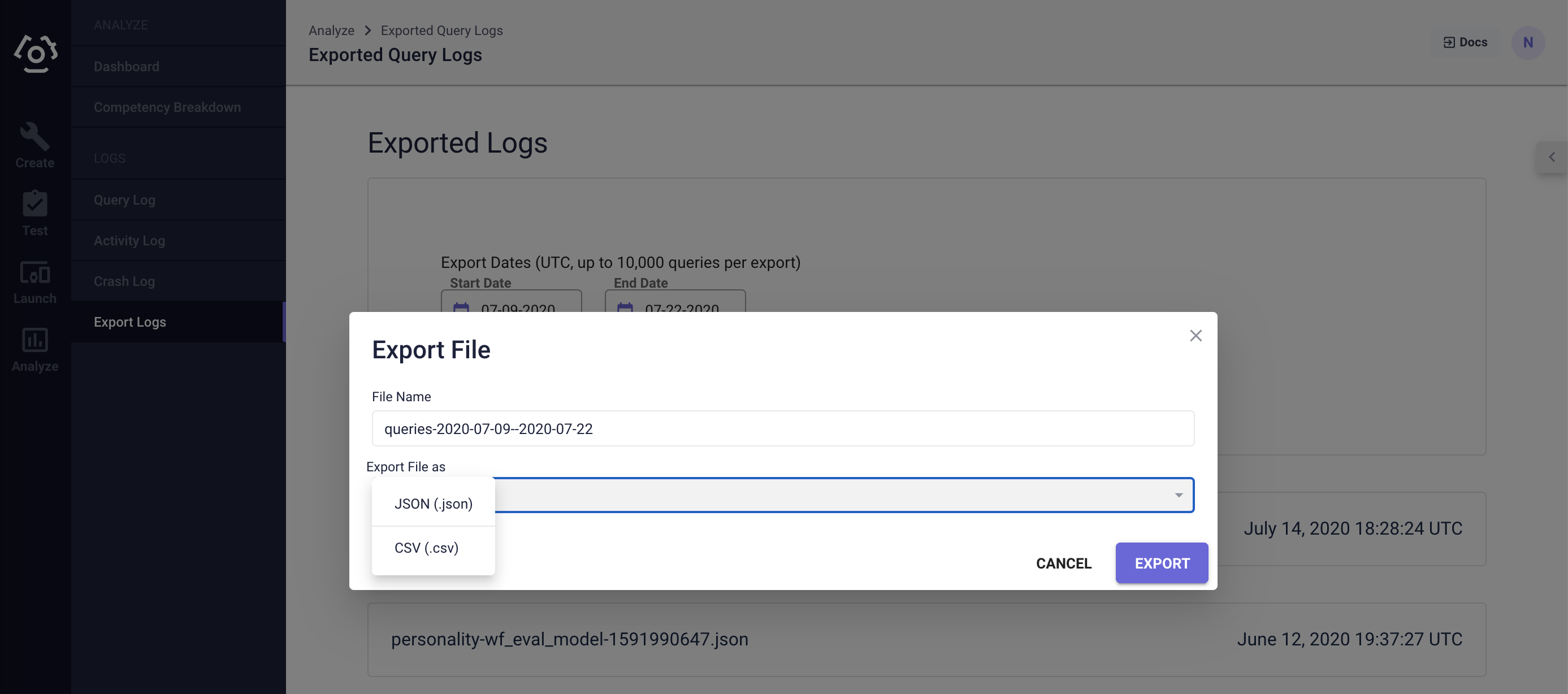
# Export Query Logs
On the export logs page, a user can choose the start and end date of the query logs that one wishes to export as well as the export file format (JSON or CSV).
# Data Format
# JSON
{
"_index": "logstash-finie-2019.12.02",
"_type": "doc",
"_id": "2c7304ab-6858-4393-8d43-f998c82a87c1",
"_score": null,
"_source": {
"host": "3dca8f95906e",
"tags": [
"querylog"
],
"@version": "1",
"extra": {
"interpreter_version": "3.6.8",
"thread_name": "Dummy-1",
"line": 246,
"logger_name": "logstash_querylog",
"interpreter": "/usr/local/bin/python3",
"logstash_async_version": "1.4.1",
"path": "/usr/local/lucida-clinc/uservices/logstash/client.py",
"process_name": "MainProcess",
"func_name": "store_query_response"
},
"pid": 601,
"program": "mod_wsgi",
"type": "python-logstash",
"@timestamp": "2019-12-02T21:00:03.352Z",
"logsource": "3dca8f95906e",
Log system specific data.
"doc": {
"OUTPUT": {
"formattedResponse": "Hello!",
"speakableResponse": "Hello!"
},
"TIMESTAMP": "2024-10-23T17:52:51.148171+00:00",
"INPUT": {
"is_repeat": false,
"project_id": "c587a871-85d1-4b51-8401-ff1c5493b9bf",
"classifier": "clean",
"certainty": true,
"intent": "clean_hello_start",
"project_name": "product_servicing",
"latency": 0.04682637006044388,
"personality_id": "c9bc5cd5-e3a4-4f2b-b2aa-518ffeb7f81e",
"platform": "web",
"external_user_id": "platform_user-978fbedc-12f0-a2b4-8afd-5c740d46b3de",
"workspace_name":"clincDefaultWorkspace",
"workspace_id":"2a875ba7-8870-4bdf-a608-e84d6b5a1b89",
"competency_id": "456f5dda-b234-49d5-be4d-38674942be53",
"classifier_state": "clean_hello",
"latencies": {
"webhook_total": null,
"total": 0.04682637006044388,
"webhook_latencies": {},
"trace": [
{
"metadata": {
"response_complete": 0.005037467926740646,
}
}
]
}
}
}
Everything in doc list are query specific data. Please reference Query Response for what each field stands for.
"bl_resp": {
"query": "I want a burger",
"qid": "2c7304ab-6858-4393-8d43-f998c82a87c1",
"slots": {
"_FOOD_MENU_": {
"values": [
{
"value": "hamburger",
"food_menu_dest": "hamburger",
"tokens": "hamburger",
"resolved": 1
}
],
"type": "string"
}
},
"lon": 0,
"project_name": "pizza_modules",
"project_id": "c587a871-85d1-4b51-8401-ff1c5493b9bf",
"state": "food_order",
"intent_probability": 0.9498837367690086,
"session_id": "3329bf2f4223412d9dba08cc115ae449",
"device": "default",
"dialog": "qnBKoS2AjVPAyXalsYvAlto+VEOwt+bj",
"time_offset": 0,
"intent": "food_order_start",
"sentiment": 0,
"lat": 0,
"external_user_id": "1"
}
Reference The Response Body section on the Business Logic page for what each field stands for.
"sentiment": 0,
"lat": 0,
"slot_probabilities": {
"_FOOD_MENU_": [
0.9999535083770752
]
},
"response_slots": null,
"slot_data": "{\"_FOOD_MENU_\": {\"type\": \"string\", \"values\": [{\"value\": \"hamburger\", \"resolved\": #, \"food_menu_dest\": \"hamburger\", \"tokens\": \"hamburger\"}]}, \"remaining_slots\": []}",
"query": "I want a burger",
"intent_raw": "food_order_start",
"visual_payload": null,
"intent_probability": 0.9498837367690086,
"competency": "food_order",
"bl_url": "https://business-logic-qsr.clinc.com",
"today": "2019-12-02T21:00:00.033Z",
"workspace_name":"clincDefaultWorkspace",
"session_id": "3329bf2f4223412d9dba08cc115ae449",
Please reference Query Response for what each field stands for.
"bl_req": {
"query": "I want a burger",
"qid": "2c7304ab-6858-4393-8d43-f998c82a87c1",
"slots": {
"_FOOD_MENU_": {
"type": "string",
"values": [
{
"food_menu_dest": "hamburger",
"tokens": "burger",
"resolved": -1
}
]
}
},
"lon": 0,
"state": "food_order",
"intent_probability": 0.9498837367690086,
"session_id": "3329bf2f4223412d9dba08cc115ae449",
"device": "default",
"dialog": "qnBKoS2AjVPAyXalsYvAlto+VEOwt+bj",
"time_offset": 0,
"intent": "food_order_start",
"sentiment": 0,
"lat": 0,
"external_user_id": "1"
},
Reference The Request Body section on the Business Logic page for what each field stands for.
}
"is_repeat": false,
"dialog": "ZPqY5/a8qRq2t9Fktd6h7hJ5pjBnFNY6",
"latencies": {
"webhook_total": 0.786525,
"webhook_latency": {},
"total": 3.3747273557819426,
"external_api": null
},
"version": "release-v0.8.21",
"intent": "food_order_start",
"is_correction": false,
"ai_version": "292fdc79-d01d-4db7-ae71-800584fbd118",
"browser": "Other",
"slot_token_ranges": {
"_FOOD_MENU_": [
{
"end": 3,
"start": 3
}
]
},
"__RAW__query": "I want a burger",
"certainty": true,
"user": "978fbedc-12f0-a2b4-8afd-5c740d46b3de",
"external_user_id": "1"
},
"OUTPUT": {
"__RAW__speakableResponse": "Okay, so you would like hamburger. Is that all you'd like?",
"speakableResponse": "Okay, so you would like hamburger. Is that all you'd like?",
"formattedResponse": "Okay, so you would like hamburger. Is that all you'd like?",
"__RAW__formattedResponse": "Okay, so you would like hamburger. Is that all you'd like?"
}
Please reference Query Response for what each field stands for.
# CSV
By default the CVS contains these fields (not necessarily in this order):
- qid
- lon
- latency
- personality_id
- device
- time_offset
- competency_id
- classifier
- platform
- RAW_slot_data
- institution_id
- classifier_state
- sentiment
- lat
- slot_data
- query
- intent_raw
- intent_probability
- competency
- today
- session_id
- is_repeat
- dialog
- extra_params
- version
- latencies
- intent
- is_correction
- ai_version
- ai_version_name
- project_name
- project_id
- workspace_id
- browser
- RAW_query
- certainty
- user
- external_user_id
- RAW_speakableResponse
- speakableResponse
- formattedResponse
- RAW_formattedResponse
- visual_data
- RAW_visual_data
Reference the Query Response page for explanations of each field.
# How to export query logs?
To export logs:
- Choose the start and end date then click Export Data.
- Choose the data format. Then Export.
- Click the newly created block to download the query logs.
Last updated: 10/24/2024